Morse code or morse code is a special way of encoding characters, which encrypts letters of the alphabet, numbers and punctuation marks using a sequence of signals: long (“dashes”) and short (“dots”).
The alphabet got its name in honor of the American inventor and artist Samuel Morse. Morse presented his invention on February 8, 1838.
Interesting fact: Morse code in its modern form was not invented by Morseand the German engineer Gerke – he improved the original Morse code, which was quite inconvenient to use.
For a long time, Morse is significant more interested in artthan technical sciences and practical inventions. However, in 1825, misfortune befell the inventor’s family. One morning, a messenger delivered a letter to Samuel informing him that his beloved wife was seriously ill. On the same day, the inventor left Washington, where he worked, and went home, but by the time he arrived, his wife had already died.
Disappointed that he didn’t get to say goodbye to his wife, Morse gave up painting and took up science, wanting to create something that would allow people to exchange messages quickly.
One day, Samuel was returning from Europe, where he studied the work of the masters of antiquity. On the way, he met a scientist who told Morse about the effect of current on a magnet and its ability to instantly travel along a long wire.
Morse was not particularly knowledgeable in electrical engineering, but he was excited by the idea of using electromagnetism to transmit signals. Using improvised means, Morse For 10 years he worked on the creation of a telegraph apparatus.
His efforts were not in vain, already in 1837 he presented a telegraph with a length of 500 meters. However, the first attempt to transmit a telegram was unsuccessful. But Morse did not give up, six months later he developed a table of symbols in the form of a combination of long and short signals. This became the Morse code, which, of course, was still improved and changed. And the final version was proposed in 1939.
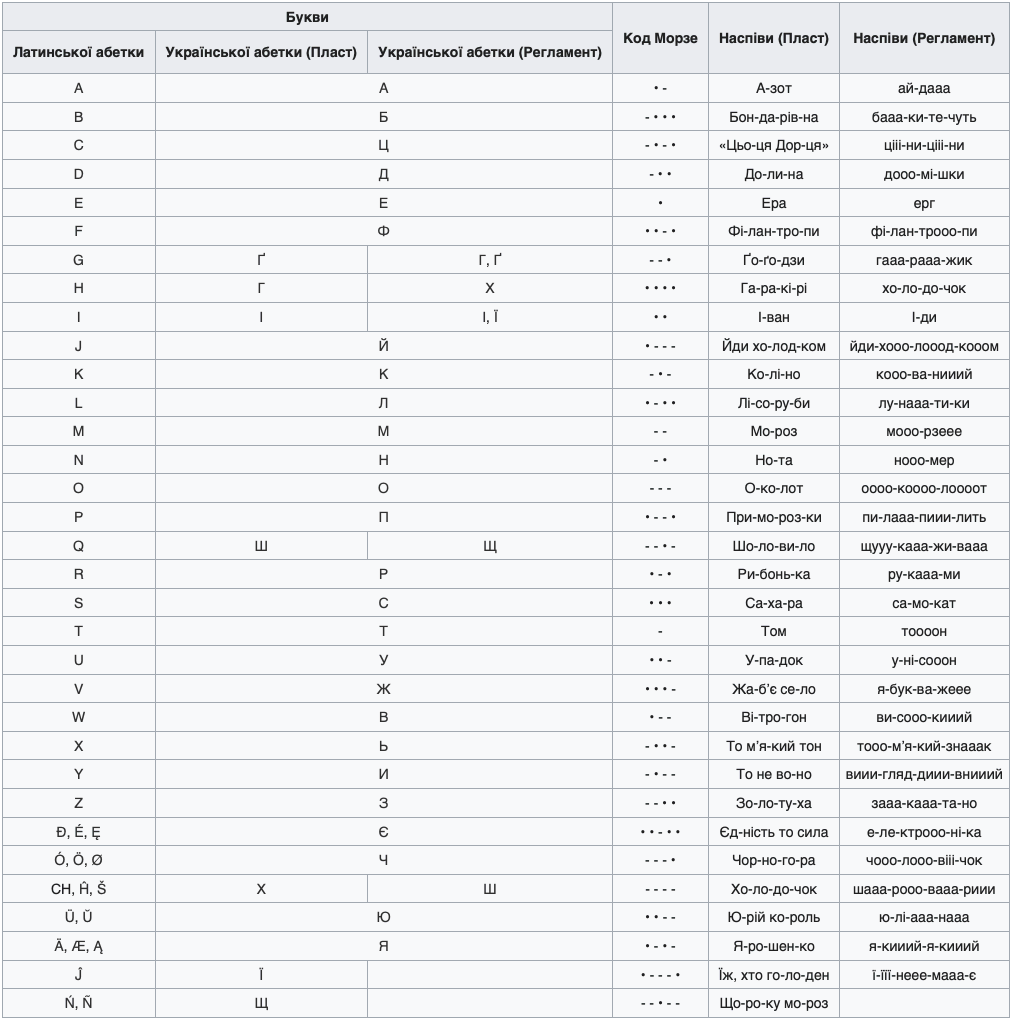
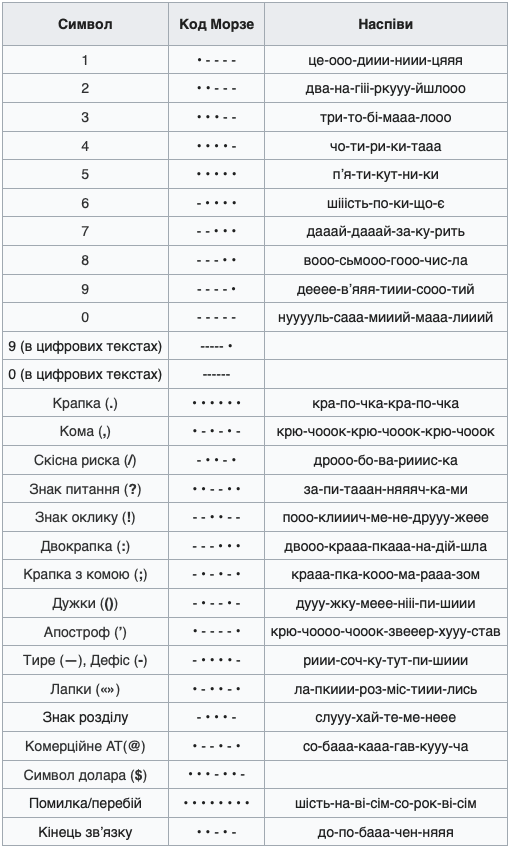
There are two main variants of Morse code in the Ukrainian language. One of them is used by Plast. The other is the standard of the Regulation of amateur radio communications of Ukraine. Verbal chants are required for auditory perception of combinations of signals. There are no strict rules here, you can use your own rhymes.
This is written in Morse code DAYTODAY
−•• •− −•−− − −−− −•• •− −•−−
Signal length standard it is considered when the long signal (dash) is three times longer than the short one (dot). The pause between signals of one symbol is equal to the duration of a short signal, the pause between symbols is equal to the duration of a long signal, and the pause between words is the duration of two long signals.
On February 6, 1900, a radio station located in the Finnish city of Kotka transmitted a wireless telegram to the icebreaker “Yermak” with an order to rescue 50 fishermen who were carried out to sea during a crisis. It was the first ever transmission of a radio signal about a distress at sea. The rescue operation was completed successfully.
SOS
The story of the rescue of the Finnish fishermen prompted the international telegraph community to introduce a single standard for transmitting a distress signal using Morse code. In 1903, letters began to be used for this CQ (come quick – come quickly). A year later, at the suggestion of the Marconi International Marine Communication Company, which produced radio transmitters, the letter D (danger) was added.
But at the same time Marconi patented this combination of letters. In connection with the transmission CQD on the air was allowed only with the help of Marconi equipment.
Another major manufacturer of radio equipment, the German company Telefunken, has also introduced its maritime distress alert system: SOE. The Germans also insisted on its use only by owners of Telefunken transmitters.
Therefore, a free international version was subsequently introduced: SOS.
With the development of technology, ships began to transmit not only mortuary language, but also human language. And for this option of emergency communication, an international standard was also introduced. In case of disaster the word is pronounced three times Mayday (mayday). After that, potential rescuers are notified of the name of the vessel and its coordinates.
However, thousands of radio operators in the world’s oceans put on their headphones at the beginning of each hour so as not to miss three such important letters for navigation: . . . – – – . . .



































